Resources
Discover a richness of information and thought leadership articles from NearbyComputing
Hype Cycle™ in Edge Computing 2023

Browse the resources you need
Enterprise Connectivity: The Power of 5G Private Networks and Edge Computing
As the requirement for private networks grows, the complexity of these solutions requires
specific tools to manage and automate the various infrastructures, network functions and
applications. To make a viable solution, a robust and easy-to-use private cloud-native core
needs to be paired with a flexible and scalable solution that can orchestrate everything from a
single site all the way to a widely distributed network, preferably from a single interface.
Edge-Enhanced Security and Monitoring – A Focus for the Energy and Utilities Industry
Energy suppliers operate across various fields and locations, frequently managing assets in remote areas lacking onsite personnel. The strategic deployment of coordinated edge devices facilitates their swift establishment in these new settings, equipped with necessary computing power while diminishing maintenance efforts and expenses.
Unlocking the Potencial of Mission-Critical Communication
In an era where quick, effective response is not just expected but vital, the importance of advanced communication systems can’t be overstated. That’s why we’re excited to introduce our latest white paper, showcasing how STREAMWIDE’s innovative mission-critical solution, Team on Mission (TOM), integrated with NearbyOne’s edge-to-cloud automation platform, revolutionizes emergency and industrial communications.
Facilitating Contactless and Automated Retail Services via Edge Technologies
Discover how retailers leverage cutting-edge technologies like edge computing for real-time, contactless services. Explore smart kiosks, cameras, and sensors enhancing performance and minimizing latency in automated retail.
Nearby Computing and Unmanned Life Forge Strategic Partnership to Lead the Future of Autonomous Systems Integration
The partnership between Unmanned Life and Nearby Computing marks a significant milestone in advancing the integration of autonomous systems and edge computing technologies. With a shared commitment to innovation and excellence, both companies are poised to lead the way in delivering transformative solutions that will shape the future of automation and drive unprecedented value for businesses worldwide.
Nearby Computing, i2i Systems & NexNet Solutions Transform the Landscape of 5G Deployment: A Swift, Reliable, and Tailored Approach
blog | press releaseBarcelona, Spain, February 2024In a groundbreaking development, Nearby Computing, the industry-leading platform for Edge Computing Orchestration and Automation, and i2i Systems, a global leader in Private 5G Networks, have signed a strategic...
Nearby Computing & Streamwide Partner to Redefine Mission-Critical Communications Deployment with Edge Automation platform
blog | press releaseBarcelona, Spain, February 2024Nearby Computing, the leading platform for Edge Computing Orchestration and Automation, and Streamwide, a prominent communications software technology provider specializing in mission-critical communications and...
Tech Mahindra and Nearby Computing Revolutionize 5G Deployment: A Rapid, Reliable, and Tailored Solution
blog | press releaseBarcelona, Spain, February 2024Nearby Computing, a pioneering force in edge automation platforms and Tech Mahindra, a global leader in technology consulting and services, have joined forces to introduce a transformative approach to 5G deployment....
Streamlining Retail Operations: The Power of Edge Computing and Automation Platforms
Blog | nearby computingWelcome to the future of retail optimization! As a CIO or Digital Transformation Manager in the retail sector, your pursuit of enhancing in-store experiences and implementing real-time measures is crucial. In this blog post, let’s explore...
Sustainability in Edge Computing: Reshaping Technology for a Greener Tomorrow
The concept of sustainability in edge computing arises from the crucial role that data centers play in providing infrastructure and resources. Traditional computing methods, which heavily rely on centralized data centers, consume a significant amount of energy to operate the system and require substantial water usage for cooling hardware.
Energy and utilities
Enabling a More Sustainable Energy Model with Edge Computing and Orchestration.
Smart cities
Edge Computing Enables the “Smart” in Smart Cities by Bringing New Concepts to the Internet of Things Network.
Smart city use cases through a 5G private city network
Solutions based on AI and IoT can bring more accurate information and help city managers to take better decisions, including real-time ones.
Create your own scalable entry-level Telco Edge Cloud
NearbyOne seamlessly orchestrates end-to-end EdgeCloud services, both at the MNO datacenter and at the public cloud level.
Fast deployment of services in remote locations
The fast and affordable access to next generation services in areas with poor network coverage.
New network paradigms for critical industries
Mission-critical networks present a cloud topology where each node has a computing capacity and a list of connections to other nodes.
Enabling the Virtual Digital Substation through Edge Computing
The technology that is deployed in Power Grid’s substations is usually appliance-based, which also implies subjugation.
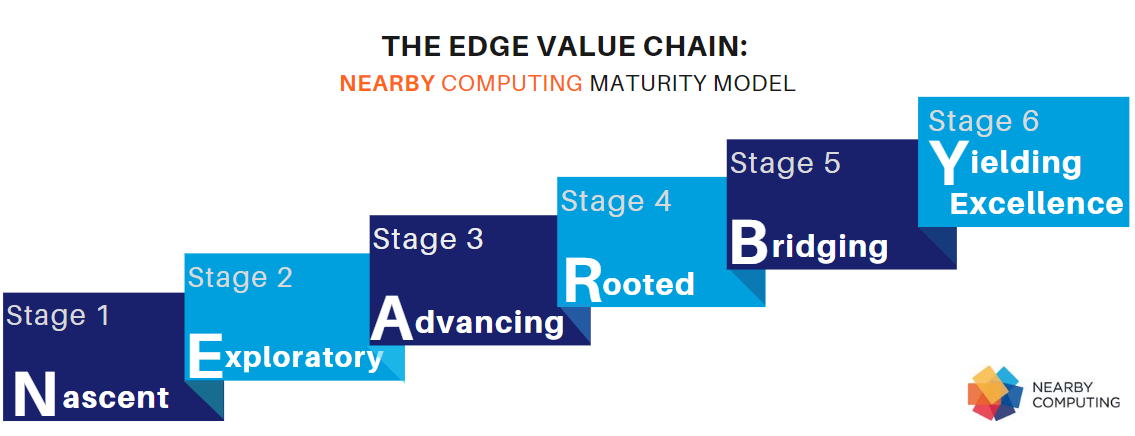
Assessing Your Digital Transformation Progress: Where Does Your Company Stand on the Edge Adoption Maturity Scale?
Nearby Computing has established a framework called “Nearby” consisting of six maturity levels for edge adoption, offering businesses a clear gauge of their progress in achieving digital transformation.
Deploy a 5G MPN in a Manufacturing Plant to Boost operations
Outdoor manufacturing plants have many restrictions that impact on the capacity to deploy networks and onboard new services to improve operations. The Critical Industry plant in Spain covers fiber optics networks and thus onboard… an area of roughly 1Km2.
Nearby Computing Named 2023 a Gartner ® Cool Vendor in Edge Computing
Nearby Computing has been recognized as a Cool Vendor in the Edge Computing market report by leading analyst firm Gartner. This recommendation is designed to highlight interesting, new, and innovative vendors, products and services. In this edition of the Cool Vendor list, Gartner selected five top companies in its category that have something unique and valuable to offer.
V2X Technology: Revolutionizing Safe and Efficient Transportation
In recent years, cars have increasingly been equipped with touchscreens and other technological features as part of their infotainment systems. This technology, called V2X, vehicles to everything, is an innovative technology that enables seamless communication between vehicles and the surrounding environment and can unleash multiple benefits such as road safety, energy savings, and traffic efficiency on the roads.
What is a 5G/Edge Lab, and Why do I need it?
By accessing a 5G/Edge Lab, companies can test and validate technological solutions, address possible technical issues, and conduct proof-of-concept testing. This lab environment permits access to cutting-edge technology, industry expertise, and resources, thereby expediting their expansion and facilitating their business growth.
Why Enterprises Can’t Afford to Ignore an Edge-to-Cloud Orchestration Platform in their digital transformation strategy
As companies undergo digital transformation, their dependence on technology increases. An Edge-To- Cloud Orchestration can unleash these challenges.
From Connectivity to Profitability: Telcos’ Guide to Monetizing New Services with Telco Edge Cloud
The Telco Edge Cloud is about to become the new and disruptive service from where a new generation of powerful use cases will be delivered to users.
Unleash Predictive Maintenance in IoT with Edge Computing: The Key to Increase Efficiency and Reduce Costs in Industry 4.0
Predictive maintenance is a critical component of Industry 4.0 that helps organizations fix issues before they cause downtime with its proactive approach that uses real-time equipment performance tracking and data analysis to predict machine failure.
Nearby Computing and Druid Software partner to deliver industry-leading yet cost-efficient and fully automated 5G+MEC solutions, to expand the adoption of Mobile Private Networks by industries
blog | press releaseBarcelona, Spain, July, 2023Nearby Computing, the industry-leader platform for Edge Computing Orchestration and Automation, and Druid Software, a global leader in Private 5G Networks, Private 4G and LTE Networks, have signed a strategic partnership...
Full-Stack Observability: Redefining the way we predict, prevent and diagnose systems
Full-stack observability refers to the ability to understand the internal state or condition of complex systems by analysing only their external outputs.
Navigating the Edge ecosystem complexity
The edge ecosystem is heterogeneous and complex, with a wide range of stakeholders. Discover how to navigate it in this post.
Nearby Computing and 6WIND join forces to offer innovative edge computing solutions
Nearby Computing and 6WIND sign a strategic partnership to jointly deploy and deliver innovate edge computing solutions for the cloud-to-edge ecosystem.
All you need to know about The CAMARA Federation APIs
This article summarizes some of the key technical aspects about CAMARA Federation APIs, from the telco and IT industries.
Nearby Computing validates the efficiency of 5G networks and edge computing in Smart Cities Emergency response
Nearby Computing has led the smart cities emergency response use case of the 5G Catalunya pilot, together with Cellnex Telecom, using technology by Lenovo.
The 5G Catalonia project receives the GSMA Foundry Excellence Award
The 5G Catalonia project has been recognised at the Mobile World Congress with the prestigious GSMA Foundry Excellence Award 2023.
Edge computing for drones
The last episode of the video series #SeriesOnEdge focuses on telco edge cloud for drones.
Edge computing will revolutionize smart city traffic management and video gaming
The sixth episode of the video series #SeriesOnEdge focuses on telco edge cloud for smart city traffic management and cloud gaming as two example use cases.
Telco edge cloud for e-shopping immersive experiences
The fifth episode of the video series #SeriesOnEdge focuses on the role of the edge orchestrator for some telco edge cloud use cases, as some e-shopping immersive experiences.
Telco edge cloud, taking the telecoms network to the next era
Through the following episodes, the video series #SeriesOnEdge takes you to telco edge cloud, which is defined as the combination of facilities for edge computing within the telecoms network.
ng-voice and Nearby Computing SL partner to deliver orchestrated network solutions to service providers and private networks
blog | press releaseThe strategic partnership will facilitate the deployment and management of end-to-end networks solutionsng-voice, leading provider of a fully containerized and cloud-native IMS solution for the telecom market, and Nearby Computing SL, provider of...
Use cases of automated guided vehicles and video analytics
The third episode of #SeriesOnEdge focuses on the use cases of automated guided vehicles and video analytics in production and maintenance.
Four edge orchestration product features developed by Nearby Computing, recognized as innovative by the European Union
The European Commission’s Innovation Radar platform includes these four innovations and highlights the market potential of this new technology.
Use cases that benefit from edge computing for private networks
This is the second episode of the new video series on edge computing and orchestration, launched by Nearby Computing together with STL Partners and Intel. Under the tittle “Series on Edge”, these videos focus on telco edge cloud and mobile private networks as two of the most ready-to-use solutions relying on this technology.